Exocrine glands histology labeled 333285
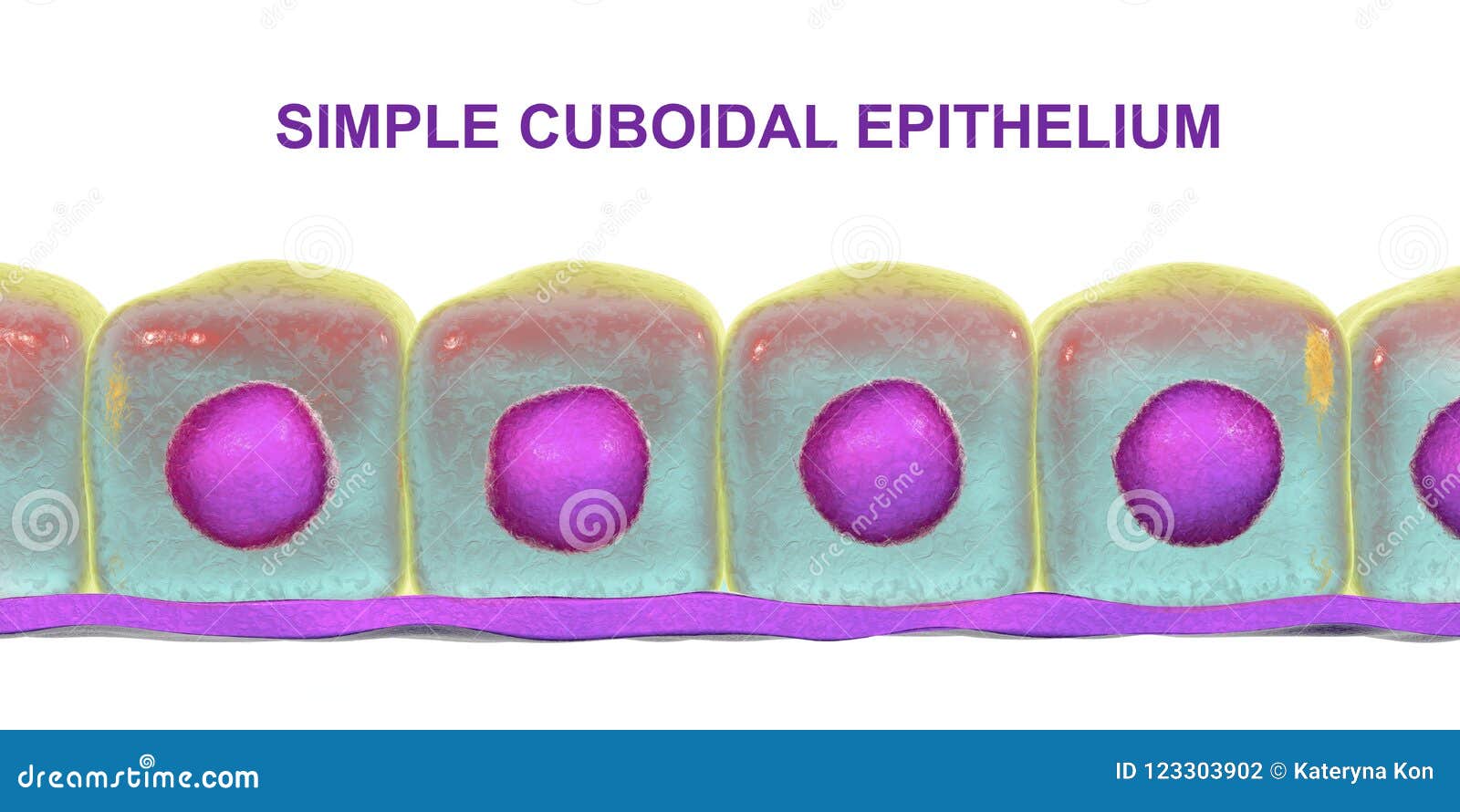
View videos describing the histological features of all the exocrine glands eg histology or the pancreas Exocrine Glands Introduction and Learning Overview, A Unicellular Gland, Classification of Glands, Mucous and Serous Secretory Units, Simple Straight Tubular Glands, Simple Coiled Tubular Glands, Simple Acinar Glands, Simple BranchedLab 2 Endocrine Anatomy & Histology Reading LABPAQ Endocrine System pages 1434 Objectives 1 To identify the major endocrine glands and tissues of the body 2 To identify the histology of the major endocrine glands and relate their structure to their function Identify the major endocrine glands and tissues of the body 3Basic anatomy of exocrine glands and lymphatic organs The average exocrine gland contains simple cuboidal epithelia ← that form grapeshaped or tubeshaped structures called acini Liquids secreted by the cells of acini enter a duct, which can be made of a simple cuboidal epithelium or simple columnar epithelium ←
Chapter 15 Page 4 Histologyolm 4 0
Exocrine glands histology labeled
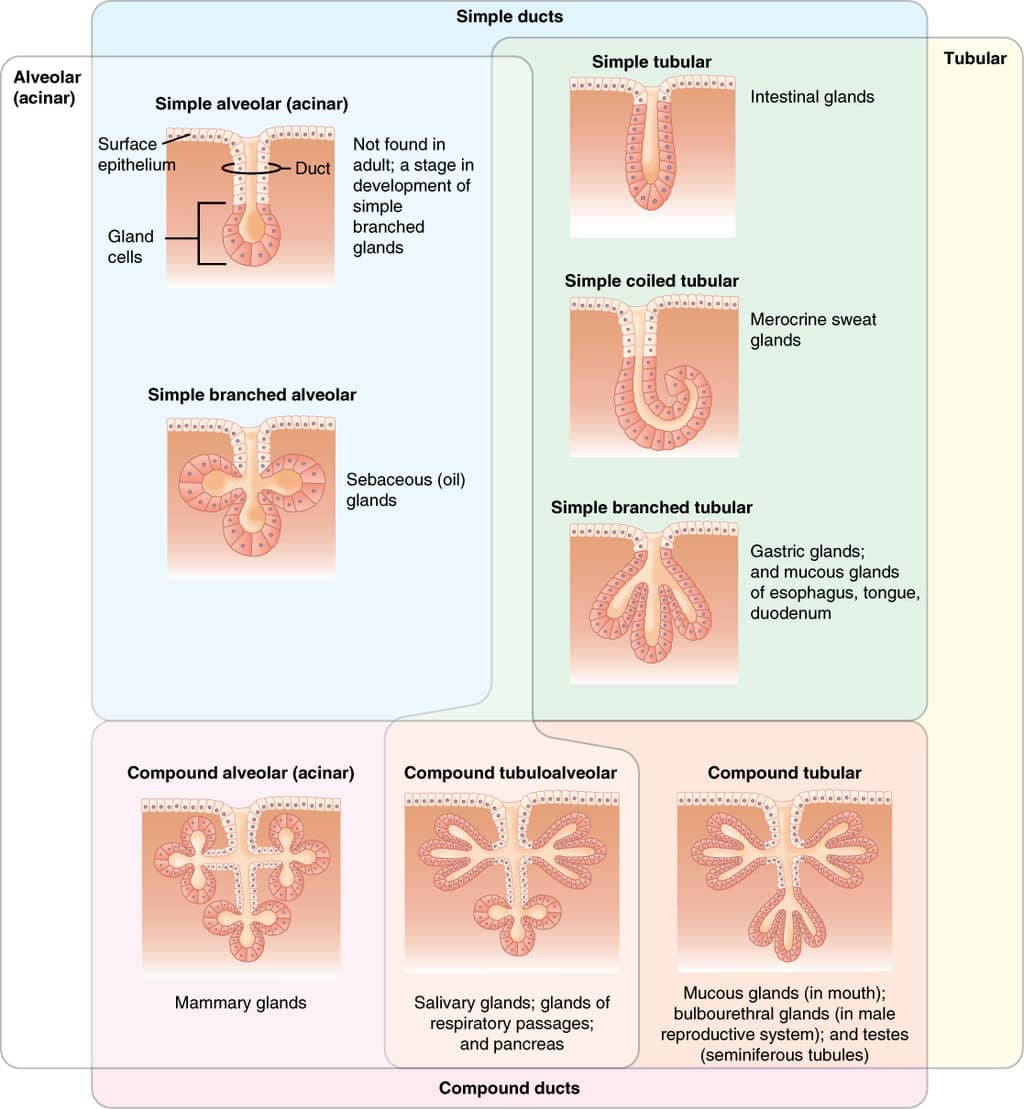
Exocrine glands histology labeled-Endocrine System Histology Pineal Gland Pineal Gland Brain Sand surrounded by Pinealocytes Low Magnification High Magnification Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe Posterior Lobe Anterior Lobe of Pituitary Gland Posterior Lobe of Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland and Parathyroid Gland Exocrine glands can be classified into a variety of categories in terms of their structure They can be categorized according to the shape of their secretory unit Secretory units shaped as a tube are referred to as tubular, whereas spherical units are referred to as alveolar or acinar, when the pancreas is involved Exocrine glands can also be comprised of both tubular and alveolar secretory



Skin The Histology Guide
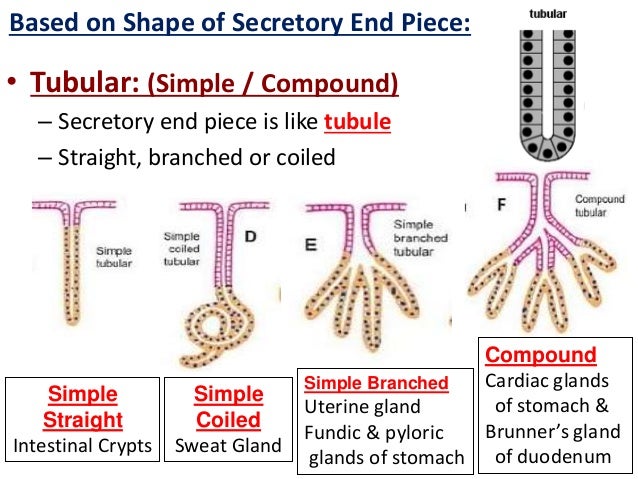
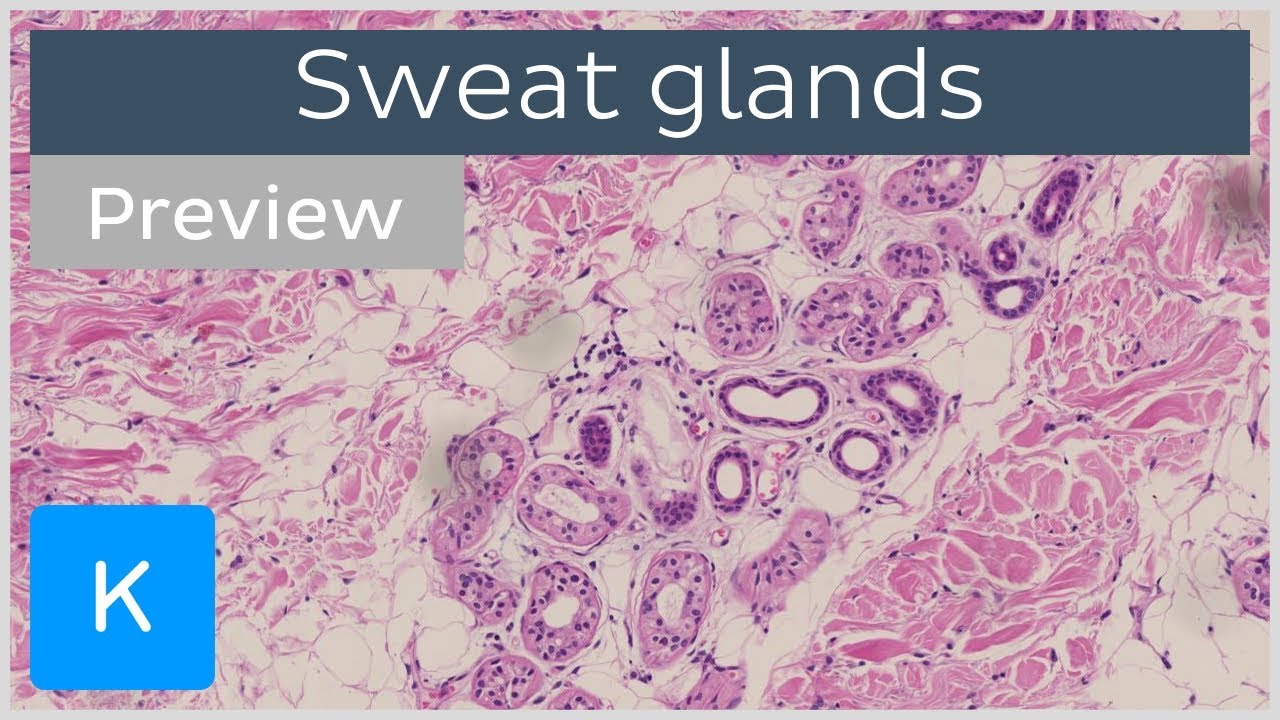
Duodenum histology slide labeled diagram In this part of the article, I will show you the duodenum histology slide labeled diagram again so that you may summarize it well The pictures showed the longitudinal section of a duodenum, where you will find almost every structureThe sweat glands are simple tubular exocrine glands that are found in the superficial hypodermis bordering on the dermis They discharge their contents onto the surface of the skin via coiled secretory ducts (see the diagram opposite)This video "Exocrine Glands" is part of the Lecturio course "Histology" WATCH the complete course on http//lecturio/exocrineglands LEARN ABOUT What is
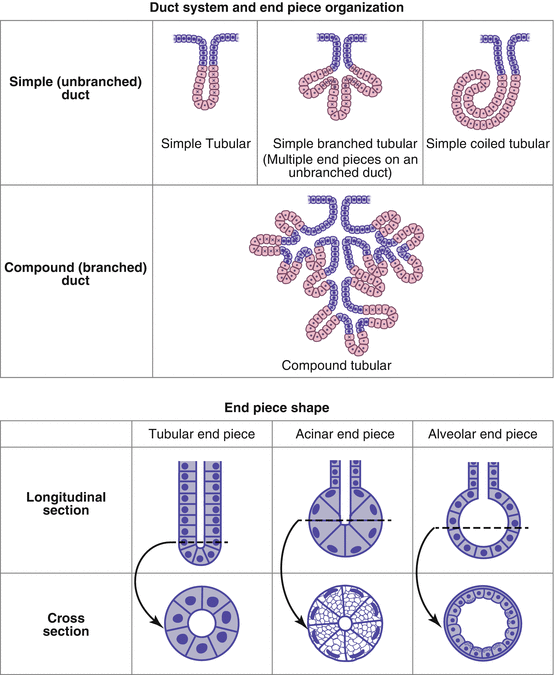
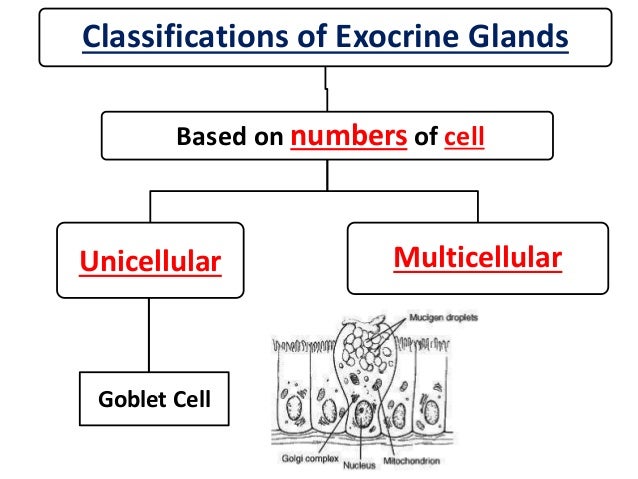
Anatomy app by Dr Ashwani Kumar http//bitly/ashwaniappSerous, Mucous and Seromucous Glands videos for NEET PG Classifications of Exocrine Glands Based on numbers of cell Unicellular Multicellular Goblet Cell 12 Multicellular Exocrine Glands 1 Based on branching pattern of ducts Simple No Branching Compound Branched 13 Multicellular Exocrine Glands 2 Based on Shape of Secretory End Piece Tubular Alveolar / Acinar Tubulo alveolar 14Serous acini Dense, basophilic, PAS intracytoplasmic secretory granules containing amylase Have central lumen that is rarely visible by H&E Mucinous / mucous acini
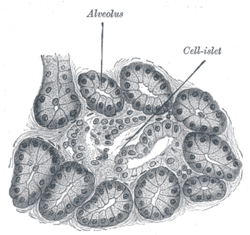
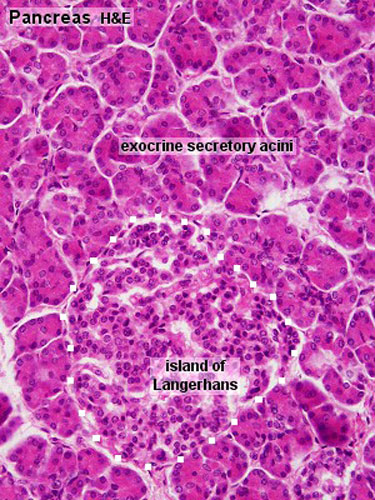
Introduction At the histological level the pancreas is made up of compound glands in "bunch of grapes" fashion The pancreas has an exocrine and endocrine component The exocrine compnent is demonstrated above in 3D with acini in "cluster of grapes" formation subtended by a duct Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD a06 Exocrine glands with ductal and acinar portions Acinar portion is serous, mucinous or mixed Acini are lined by luminal cells, which are enclosed by myoepithelial cells;Keratinization covering of dry, tough material that prevents water from passing non keratinization epithelial remains moist and soft glandular epithelium specialized cells that produce and secrete substances exocrine glands secretes products into ducts that open onto surfaces sweat glands endocrine glands



Structure Of Glands Exocrine Endocrine Histology Teachmephysiology



Mixed Exocrine Gland Stock Image Image Of Histology
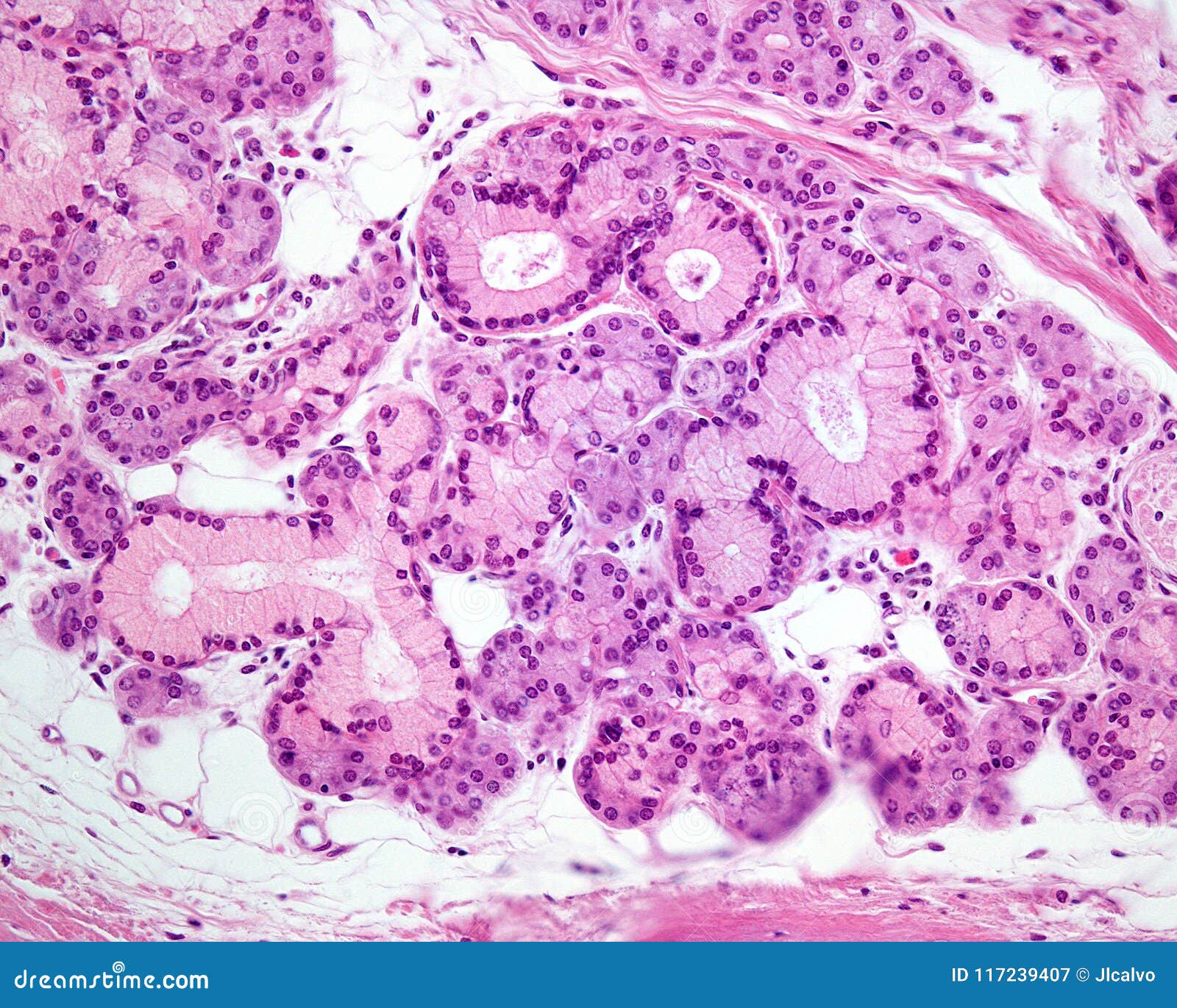
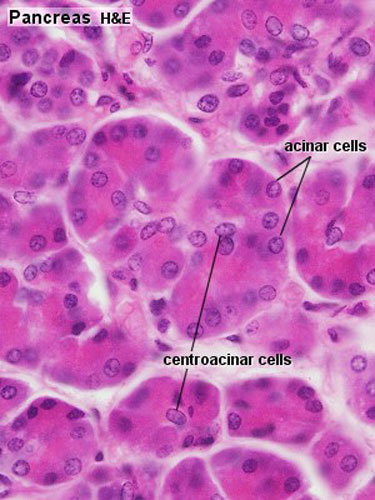
As in salivary glands, intercalated ductal cells in the pancreas contribute bicarbonate ions (sodium and water follow passively) to the exocrine secretory product However, unlike salivary glands, there are no striated ducts in the pancreas to recover sodium, so the final product is rich in both sodium and bicarbonate (as opposed to saliva inDescribe the histology of the exocrine glands of the Pancreas The exocrine glands of the Pancreas are composed of 3 different cell types and each has a specific function 1 Acinar Cells These cells secrete Zymogen Granules full of digestive enzymes when stimulated and are arranged inComparisons of current secretion and transport models in the mammary gland, exocrine pancreas and salivary gland indicate that significant differences exist between the mammary gland and other exocrine organs in how proteins and lipids are packaged and secreted, and how fluid is transported Mammary Glands, Human / anatomy & histology



Acinus Wikipedia



Skin The Histology Guide
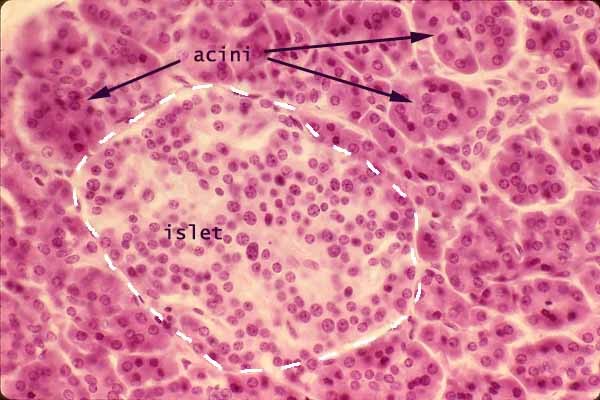
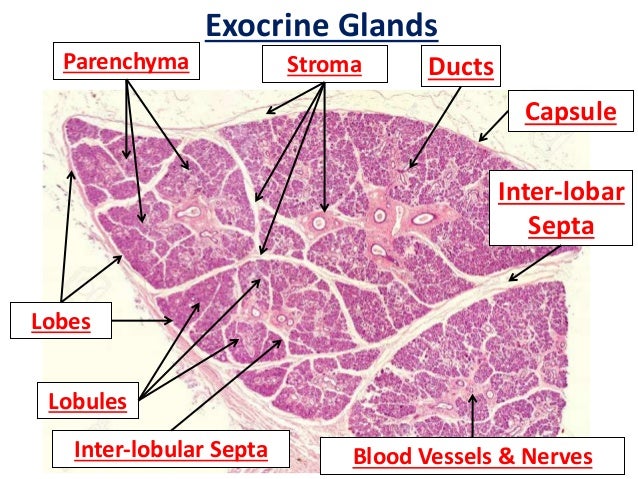
4 rows The exocrine component of the pancreas makes up about 98% of the pancreatic tissue It isCovers body surface, lines body cavities, lines external/internal organs avascular ( no blood vessels) Functions of Epithelial Tissue protection, secretion, excretion, absorption, filtration, sensation basement membrane anchors an epithelium to the connective tissues Simple Epithelia only one layer of cellsFigure 51 Basic anatomy of an exocrine gland Basic anatomy of exocrine glands and lymphatic organs The average exocrine gland is composed of simple cuboidal epithelial cells that form grapeshaped structures called acini (although other glands have tubeshaped ends) These grapeshaped structures are where secretions are produced




Lab 6 Urinary Exocrine And Endocrine Histology




Tubular Gland An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
A comprehensive account of the anatomy and histophysiology of the ecdysial glands of Philosamia ricini during post embryonic development has been given The study clearly indicates an increase in number of cells in each larval instar by endomitosis The maximum number of Please, try to identify the following histology slides of exocrine and endocrine glands – #1 Parotid salivary gland histology slide #2 Submandibular salivary gland slide #3 Sublingual gland histology slide #4 Mammary gland histology slide #5 Pituitary histology slide #6 Thyroid gland histology slide #7 Adrenal gland microscope slide




Electron Micrograph Of Part Of A Serous Acinus In A Parotid Gland



Biology 2404 Tissues



Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Stock Illustration Illustration Of Cell



Blue Histology Epithelia And Glands



Submandibular Gland




Pancreas Histology Identifying Features With Labeled Slide Images Anatomylearner The Place To Learn Veterinary Anatomy Online



Skin The Histology Guide




Histology Endocrine Glands Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
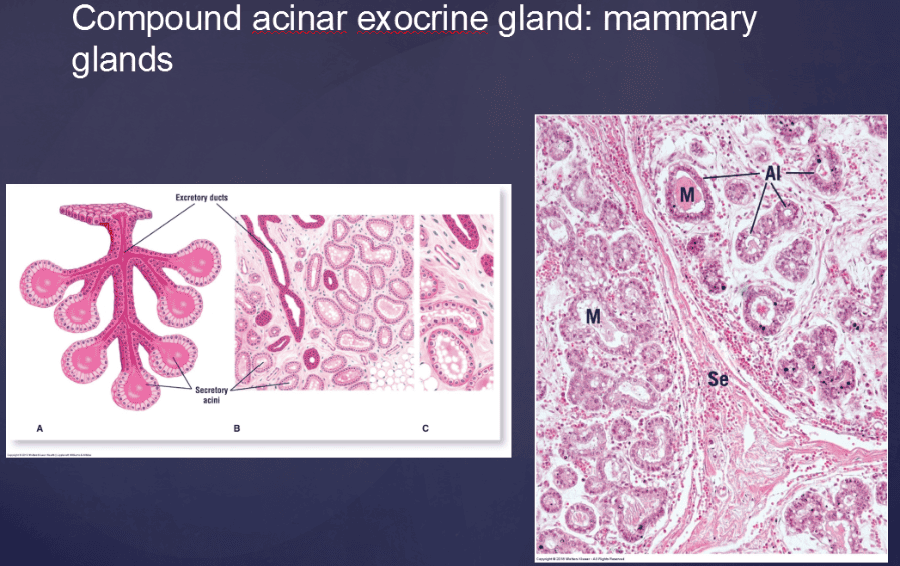



Print Vertibrate Histology Test 1 Flashcards Easy Notecards



Blue Histology Epithelia And Glands
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/2471/shYLtWdYUjK3qRvwMzK4Q_Compound_tuboalveolar_mixed_salicary_gland.png)



Glands Anatomy And Clinical Notes Kenhub
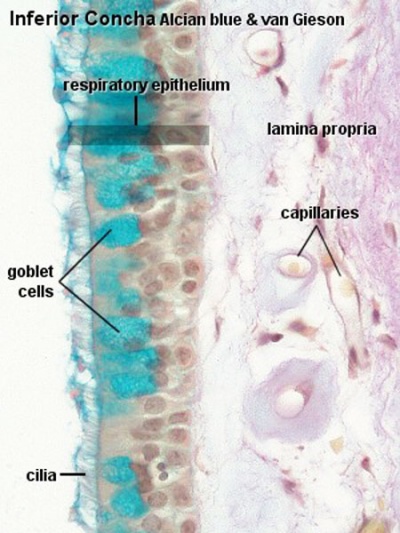



Anat2241 Glandular Epithelia Embryology




Exocrine Glands Of The Integumentary System Youtube



Chapter 15 Page 4 Histologyolm 4 0
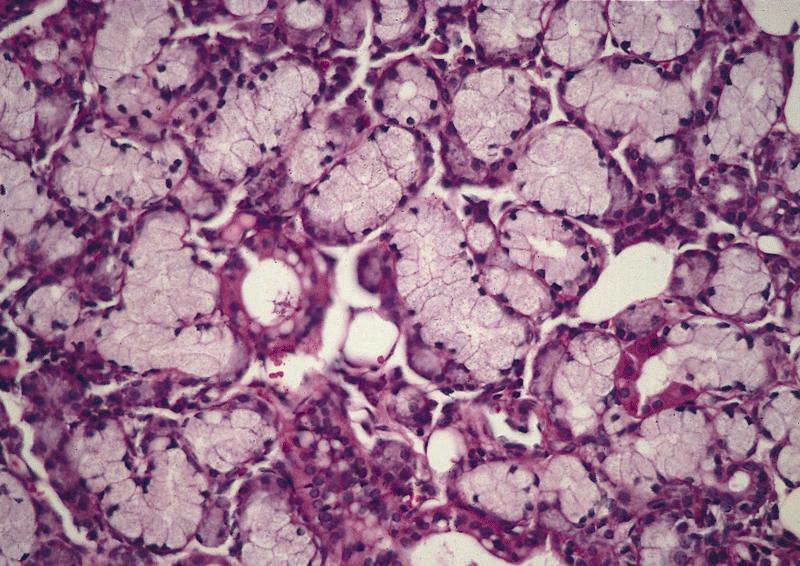



Pathology Outlines Anatomy Histology



Blue Histology Epithelia And Glands
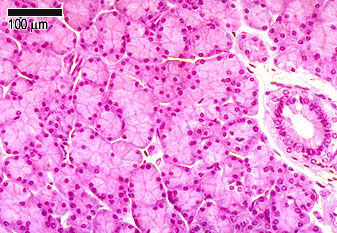



Glandular Tissue The Histology Guide



Sweat Gland Wikipedia



Skin The Histology Guide
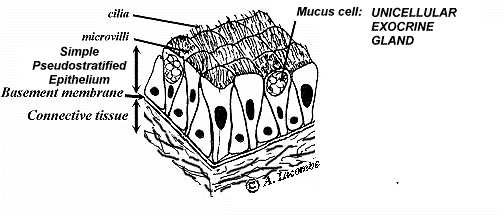



Al S Tutorial Histology Epithelium Glandular Epithelia




Exocrine Pancreas Google Search Pancreas Histology Slides Endocrine System
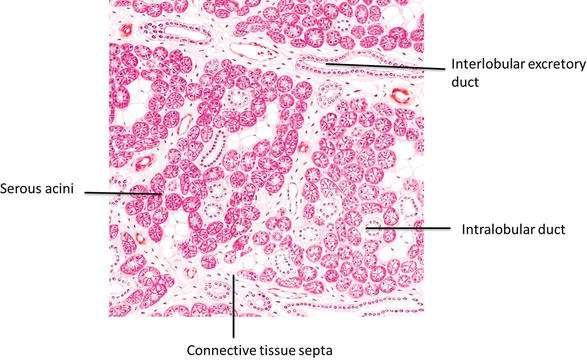



Salivary Glands Intechopen



Study Notes
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/2472/r3yQf6wxyufP1joSAhl7eg_Mixed_seromucous_glands.png)



Glands Anatomy And Clinical Notes Kenhub




Picture Test In Histology Of The Endocrine Glands Youtube



Skin Lab
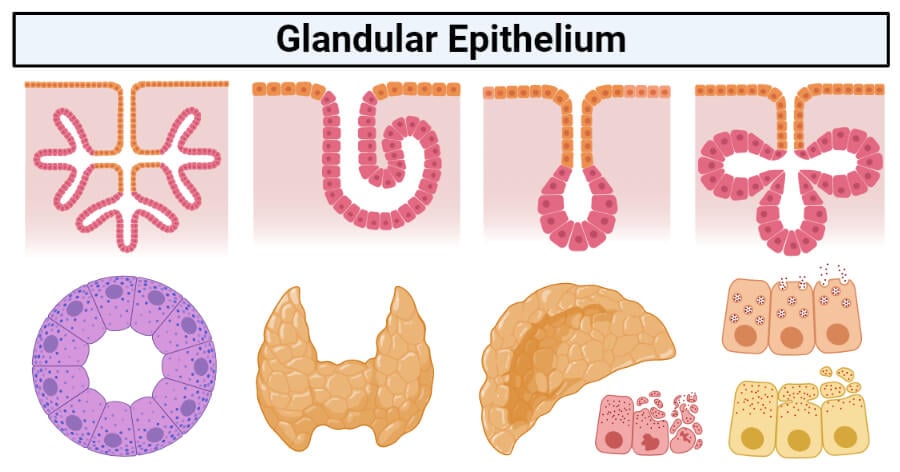



Glandular Epithelium Definition Structure Functions Examples
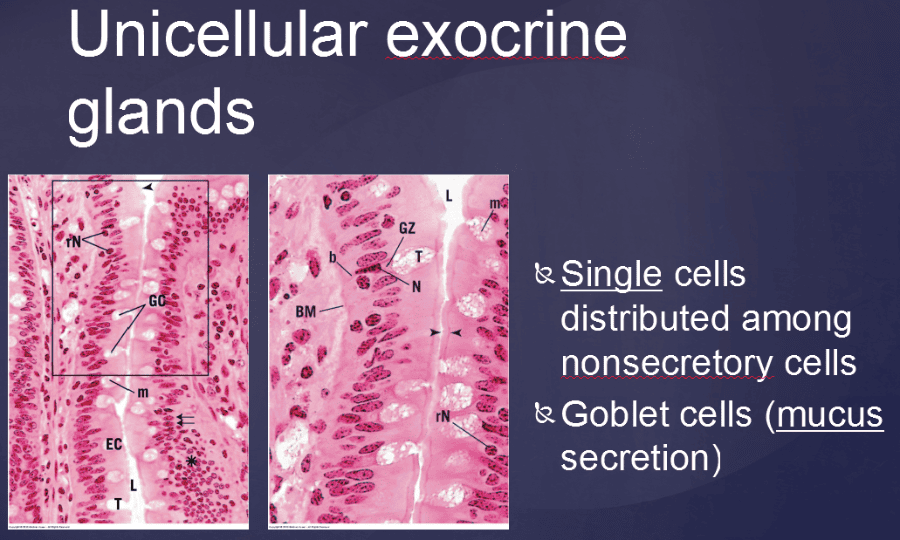



Print Vertibrate Histology Test 1 Flashcards Easy Notecards
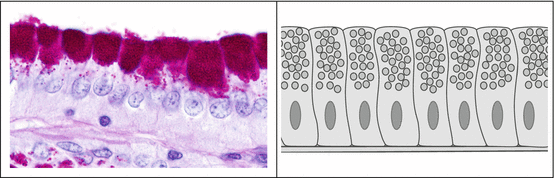



Glandular Epithelium And Glands Springerlink




Lab 6 Urinary Exocrine And Endocrine Histology
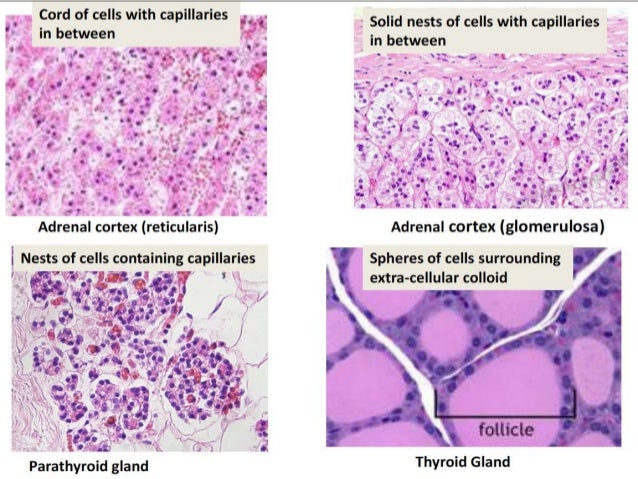



Glands Histology



Glands Histology




Animal Tissues Epithelium Salivary Gland Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology




Salivary Gland An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Blue Histology Epithelia And Glands



Sweat Glands Preview Histology Function Human Anatomy Kenhub Youtube



Parotid Gland



Pancreatic Histology Exocrine Tissue




Salivary Gland An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Morphology Of Salivary And Lacrimal Glands Intechopen



Glandular Epithelium




Morphology Of Salivary And Lacrimal Glands Intechopen



Study Notes




Pin On Histology Slides




Sebaceous Glands An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Pancreatic Histology Exocrine Tissue



Histology At Siu




Mammary Gland Histology Lactating And Non Lactating Histological Characteristics Anatomylearner The Place To Learn Veterinary Anatomy Online




Pancreas Histology Pancreas Labels Histology Slide Medical School Studying Histology Slides Medical Education



Glandular Epithelium And Glands Springerlink



Chapter 15 Page 5 Histologyolm 4 0



Parotid Gland




Tubular Gland An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Glands Histology




Endocrine




Light Micrograph Of A Resting Mammary Gland At Higher Magnification




Salivary Gland An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Animal Tissues Epithelial Tissue Glands Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology




Lacrimal Gland Histopathology H E Staining Of A Normal Lacrimal Gland Download Scientific Diagram




Intercalated Duct An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Chapter 15 Page 7 Histologyolm 4 0




Exocrine Gland Wikipedia




Tubular Gland Wikipedia




Microscope Slides Of Cells And Tissues Histology Guide




Epithelial Tissues Exocrine Glands Quiz Digital Histology



Basic Histology Short Columnar Epithelium Exocrine Glands



Glands Histology



Gastrointestinal Tract Pancreas Histology Embryology



Epithelia The Histology Guide




Pin By Dany Levy On Biology Medicine Histology Slides Medical Coding Pancreas



Chapter 15 Page 4 Histologyolm 4 0




Holocrine Wikipedia



File Pancreas Histology 002 Jpg Embryology




Histology Of Pancreas Youtube
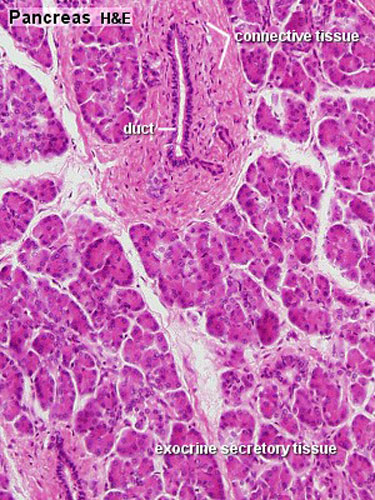



Gastrointestinal Tract Pancreas Histology Embryology



Animal Tissues Epithelial Tissue Glands Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology
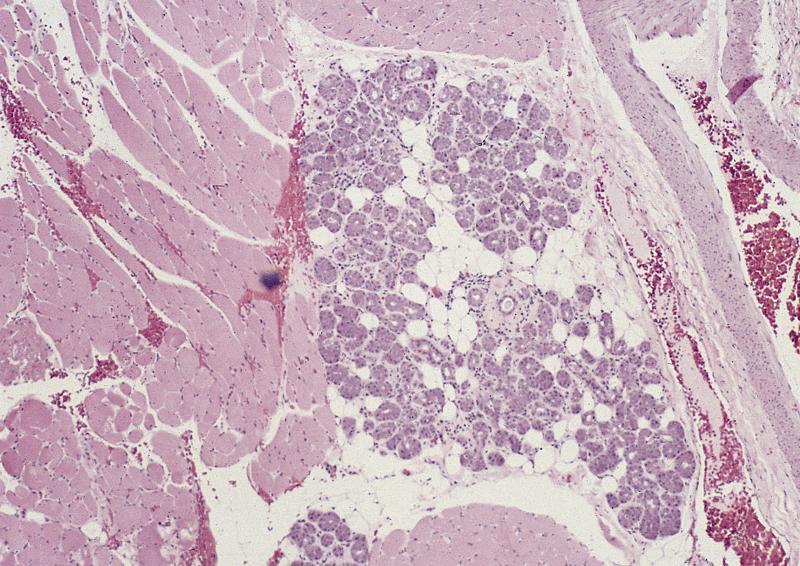



Pathology Outlines Anatomy Histology




Histology Of The Pancreas Endocrine And Exocrine Youtube




Epithelial Glands Basicmedical Key




Lab 6 Urinary Exocrine And Endocrine Histology




Lab 6 Urinary Exocrine And Endocrine Histology



Kgmu Org



Liver And Pancreas



Epithelia The Histology Guide



Oral The Histology Guide
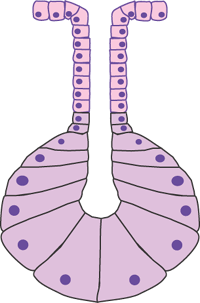



Epithelia The Histology Guide



1



Pancreatic Histology Exocrine Tissue




Salivary Gland Histology Parotid Submandibular And Sublingual Glands Structure Anatomylearner The Place To Learn Veterinary Anatomy Online
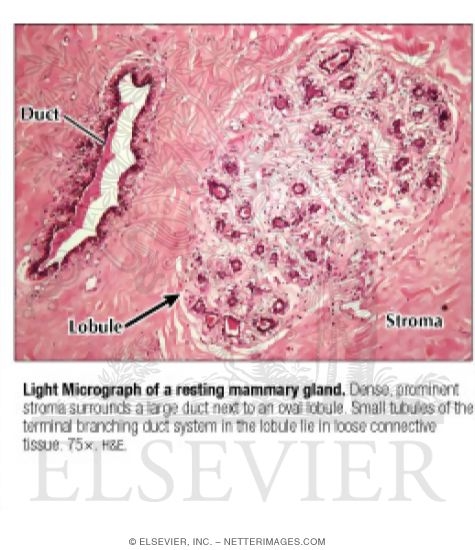



Light Micrograph Of A Resting Mammary Gland



Kgmu Org



Blue Histology Epithelia And Glands



Exercise 4 Epithelium




General Histology Knowledge Amboss



Submandibular Gland
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3778/mNlBYB0eHlYXptgna1cnQ_Sweat_glands.png)



Sweat Glands Structure And Function Kenhub



Chapter 15 Page 7 Histologyolm 4 0
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1881/CPsIC67xuz6pLt6JhAM6Wg_pancreas-histology_english.jpg)



Pancreas Histology Exocrine Endocrine Parts Function Kenhub
コメント
コメントを投稿